Projects ECG (Electrocardiogram) Monitoring
Myocardial infarction III
In this post, I investigated the changes immediately after MI and after recovery in four myocardial infarctions:
infero-lateral, antero-septal, postero-lateral and infero-postero-lateral.
1. infero-lateral
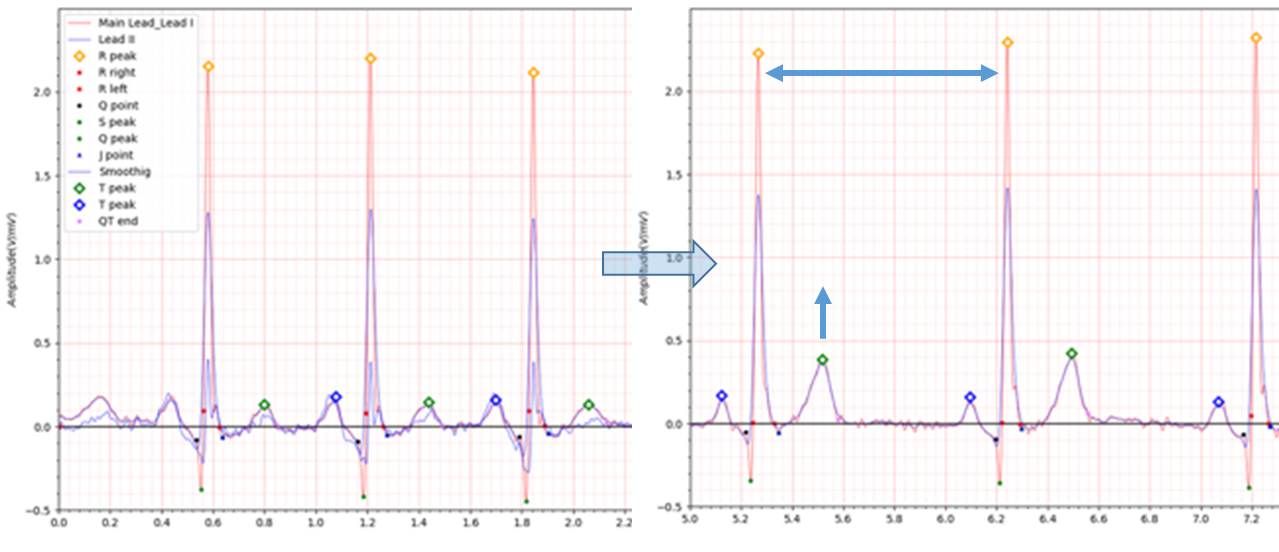
Fig.1 patient017 s0053lre:19/11/1990 -> s0075lre: 10/12/1990
- age: 60
- sex: male
- ECG date: 19/11/1990
- Infarction date (acute): 18-Nov-90
- Previous infarction (1) date: 01-Jan-86
- Reason for admission: Myocardial infarction
- Acute infarction (localization): infero-lateral
- Former infarction (localization): inferior
- Additional diagnoses: Arterial hypertension
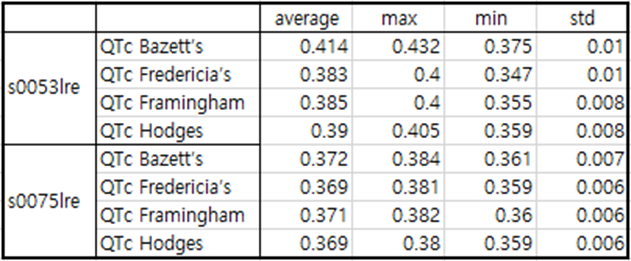
Table 1 patient017
In the case of patient017, a fairly deep Q wave and a distinct J wave are observed. In the case of patient017, infero-lateral MI occurred 4 years after experiencing inferior MI.
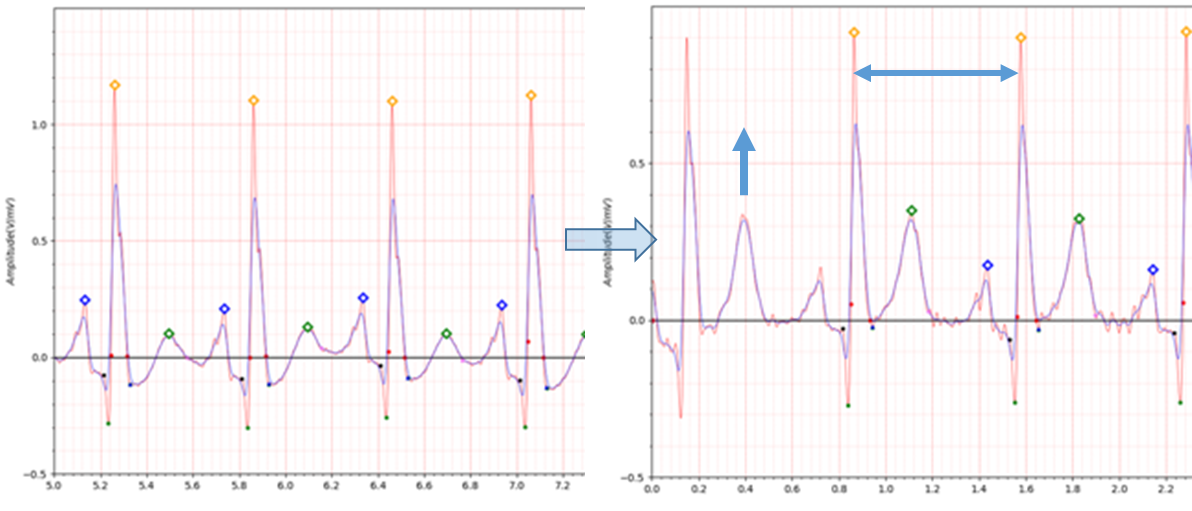
Fig.2 patient041 s0132lre: 25/02/1991 -> s0276lre: 23/03/1992
- age: 65
- sex: male
- ECG date: 25/02/1991, Infarction date (acute): 24-Feb-91
- Reason for admission: Myocardial infarction
- Acute infarction (localization): infero-lateral
- Former infarction (localization): postero-lateral, 01-Jan-86
- Additional diagnoses: Gastric ulcers Hyperglykemia
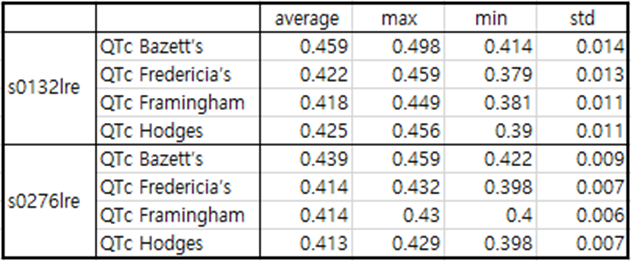
Table2 patient041
In the case of patient041, a fairly deep Q wave and a distinct J wave are also observed. In the case of patient041, infero-lateral MI occurred 5 years after experiencing postero-lateral MI.
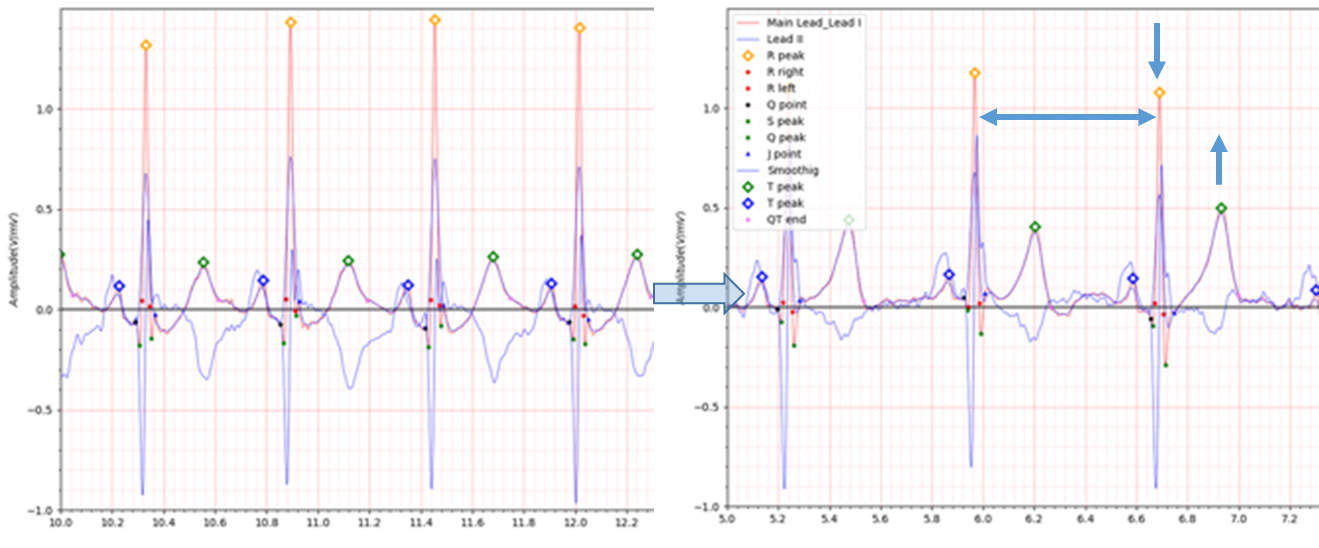
Fig.3 patient045 s0147lre: 04/04/1991 -> s0217lre: 09/09/1991
- age: 44
- sex: male
- ECG date: 04/04/1991, Infarction date (acute): 03-Apr-91
- Reason for admission: Myocardial infarction
- Acute infarction (localization): infero-lateral
- Former infarction (localization): no
- Additional diagnoses: Hyperlipoproteinemia Type IV
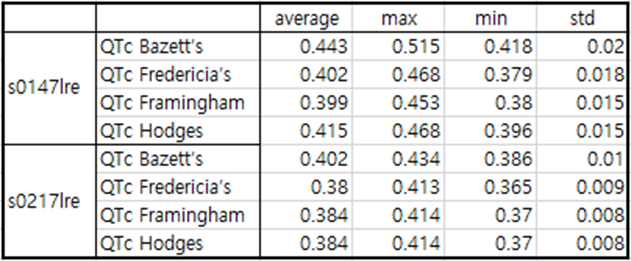
Table3 patient045
In the case of patient045, a Q wave of about -0.2 and a distinct J wave are observed immediately after MI occurs.
However, 5 months after the MI occurred, the depth of the Q wave decreased to about -0.05 to 0.1.
A fairly deep Q wave was observed in Lead II, but the J wave disappeared in Lead I after MI recovery.
J point shows an irregular pattern within the range of -0.5 to 0.8. In this case, it is difficult to judge that the
electrocardiogram is from a patient who has previously suffered MI based solely on the electrocardiogram.
In order to ensure accuracy of single-lead ECG devices, it is necessary to recommend measurement with other leads in
such ambiguous cases.
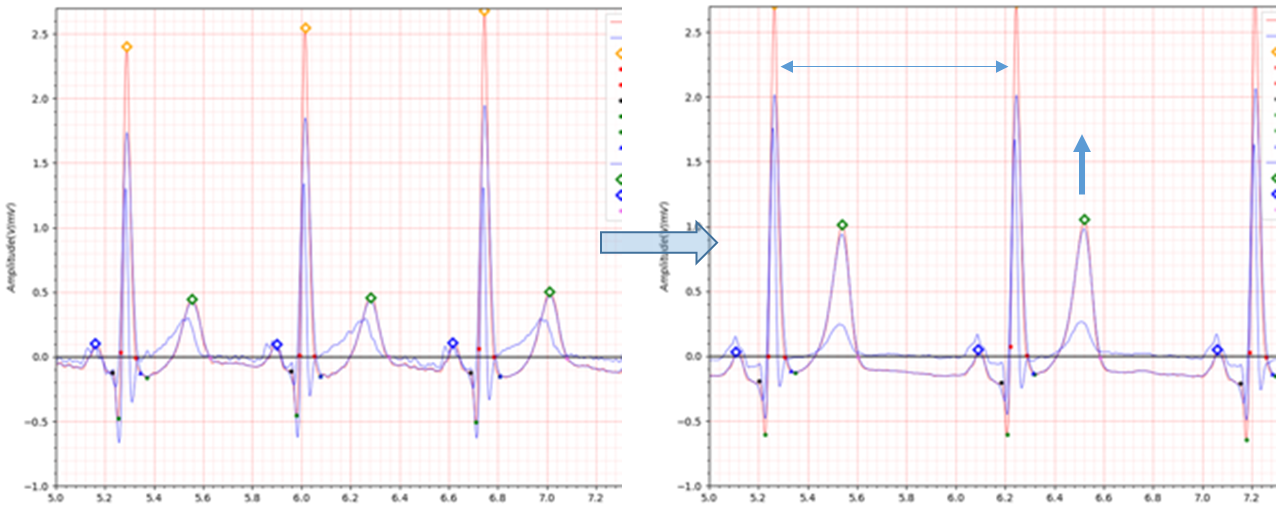
Fig.4 patient054 s0192lre: 10/06/1991 -> s0217lre: 12/09/1991
- age: 47
- sex: male
- ECG date: 10/06/1991, Infarction date (acute): 10-Jun-91
- Reason for admission: Myocardial infarction
- Acute infarction (localization): infero-lateral
- Former infarction (localization): no
- Additional diagnoses: no
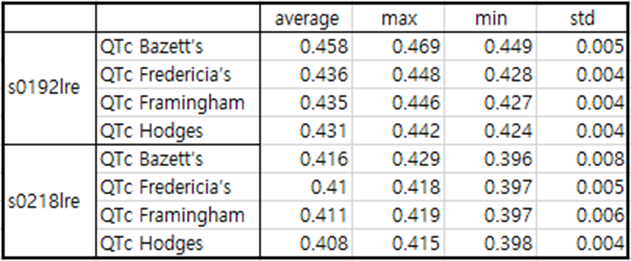
Table4 patient054
In the case of patient054, a fairly deep Q wave is observed and the S wave does not exist.
Also, after the T wave, the isoelectric line drops below -0.1.
What the four infero-lateral cases had in common was that the T wave was elevated and QTc was steadily decreased during
the recovery period after MI.
2. antero-septal
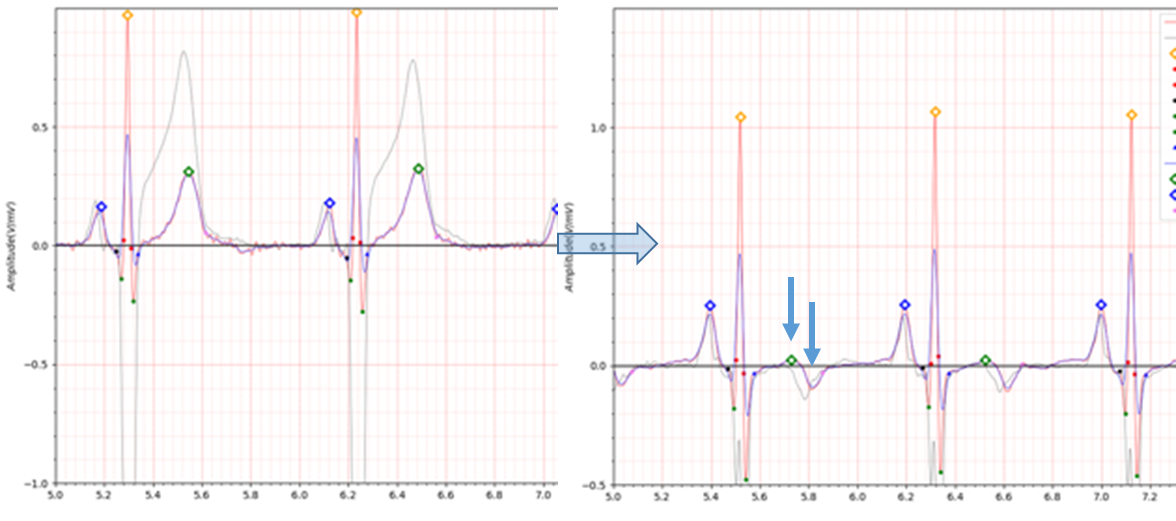
Fig.5 patient024 s0083lre: 21/12/1990 -> s0094lre: 09/01/1991
- age: 52
- sex: male
- ECG date: 21/12/1990 Infarction date (acute): 20-Dec-90
- Reason for admission: Myocardial infarction
- Acute infarction (localization): antero-septal
- Former infarction (localization): no
- Additional diagnoses: Gastritis Rheumatoid arthritis
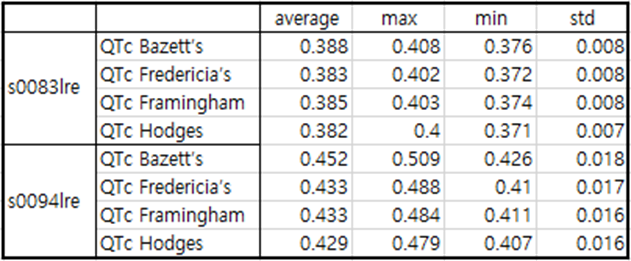
Table5 patient024
patient024 is a case of antero-septal MI.
The T wave in the ECG during the recovery period after MI is reversed. Additionally, it can be seen that QTc is
significantly prolonged.
Q wave shows a fairly low value of -0.2.
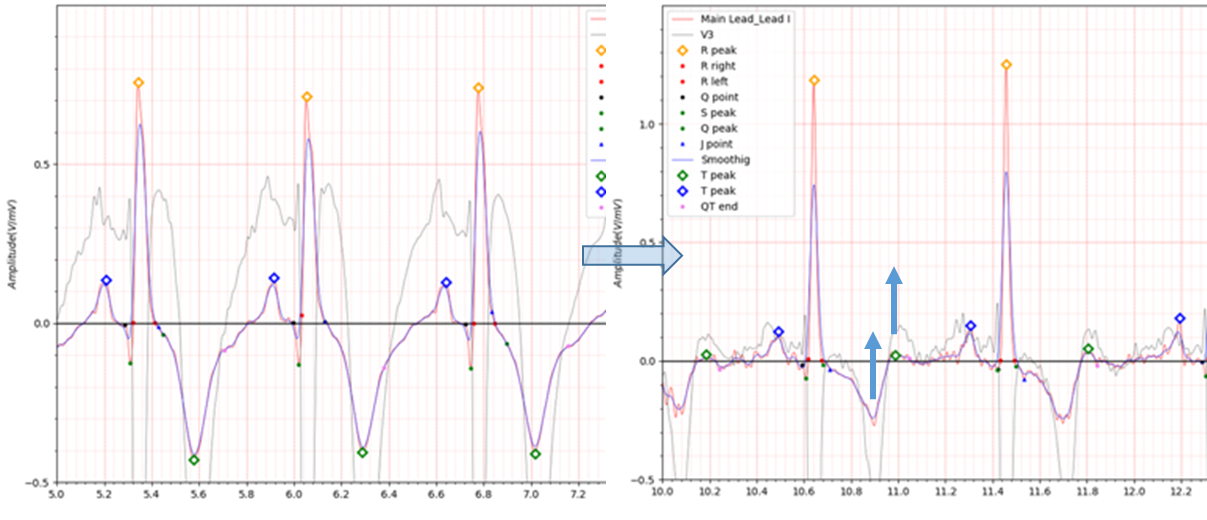
Fig.6 patient030 s0099lre: 16/01/1991 -> s0153lre: 12/04/1991
- age: 63
- sex: male
- ECG date: 16/01/1991 Infarction date (acute): 15-Jan-91
- Reason for admission: Myocardial infarction
- Acute infarction (localization): antero-septal
- Former infarction (localization): no
- Additional diagnoses: no
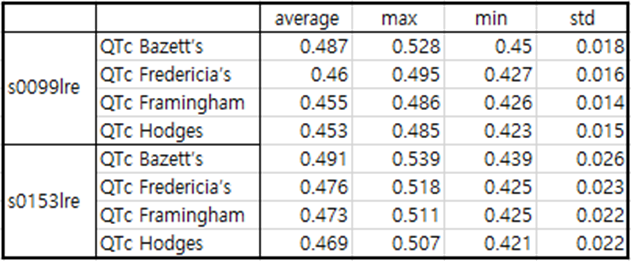
Table6 patient030
patient030 is a case of antero-septal MI.
Immediately after MI occurs, the Q wave depth is around -0.1 to -0.15, and the T wave is reversed with a significant
depth reaching -0.4. In an electrocardiogram 3 months after MI, the depth of the Q wave is about -0.05 and the depth of
the inverted T wave is about -0.25.
QTc is significantly prolonged both immediately after MI and during recovery.
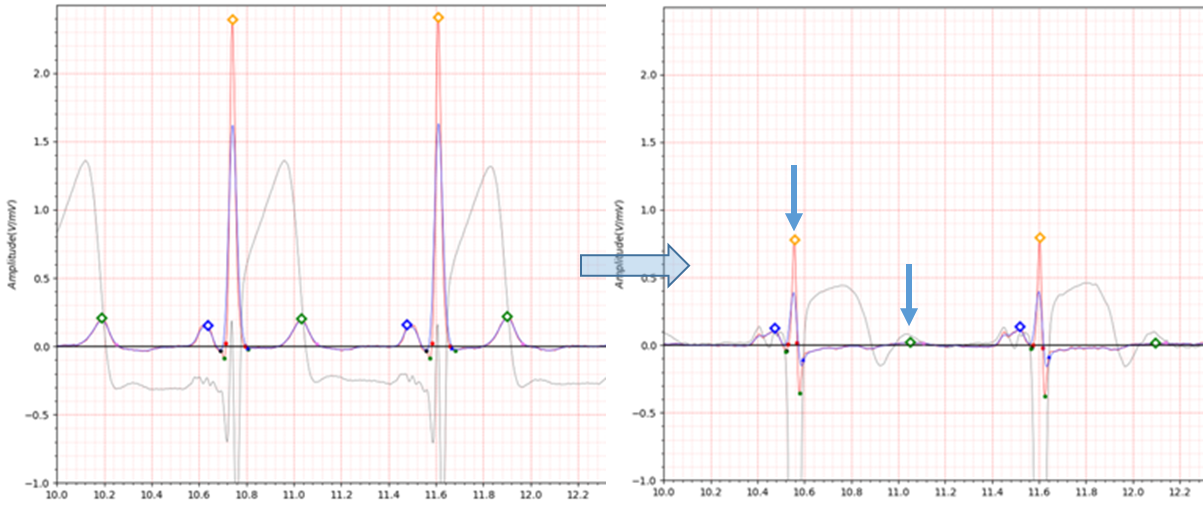
Fig.7 patient082 s0267lre: 16/03/1992 -> s0320lre: 05/08/1992
- age: 65
- sex: male
- ECG date: 16/03/1992, Infarction date (acute): 16-Mar-92
- Reason for admission: Myocardial infarction
- Acute infarction (localization): antero-septal
- Former infarction (localization): no
- Additional diagnoses: Arterial hypertension, Hypercholesterolemia, Chronic hepatitis
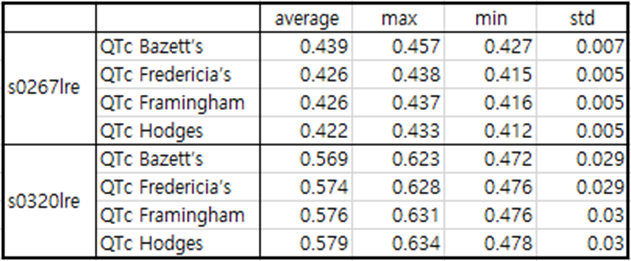
Table7 patient082
patient082 is a case of antero-septal MI.
Immediately after MI occurs, the Q wave has a depth of about -0.1 and the J wave is observed.
The electrocardiogram taken about 5 months after the MI showed a flat T wave and QTc was significantly prolonged.
3. postero-lateral
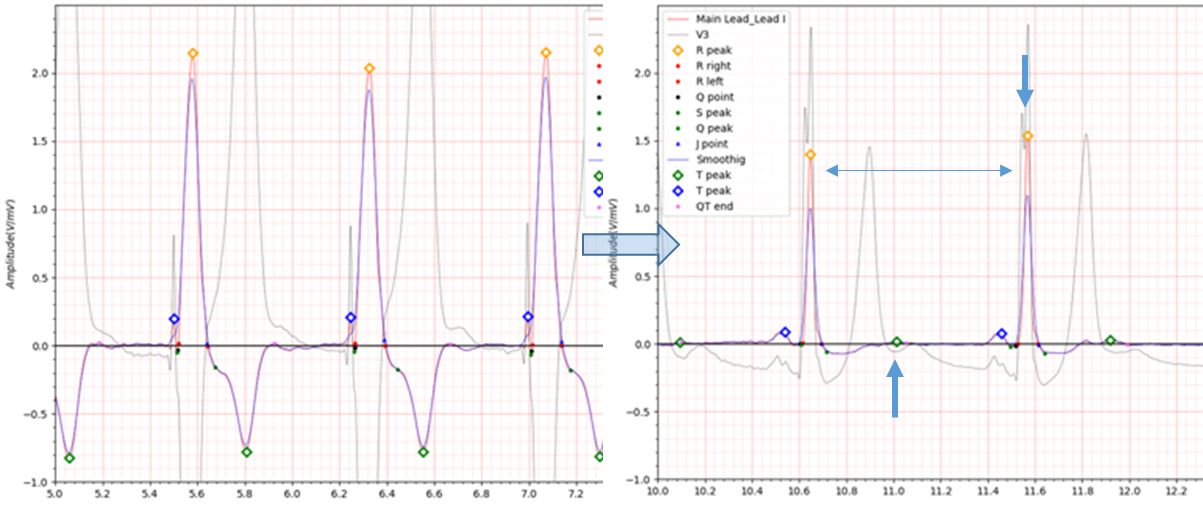
Fig.8 patient079 s0256lre: 19/02/1992 -> s0269lre: 17/03/1992
- age: 75
- sex: male
- ECG date: 19/02/1992, Infarction date (acute): 18-Feb-92
- Reason for admission: Myocardial infarction
- Acute infarction (localization): postero-lateral
- Former infarction (localization): no
- Additional diagnoses: Diabetes mellitus, Renal insufficiency
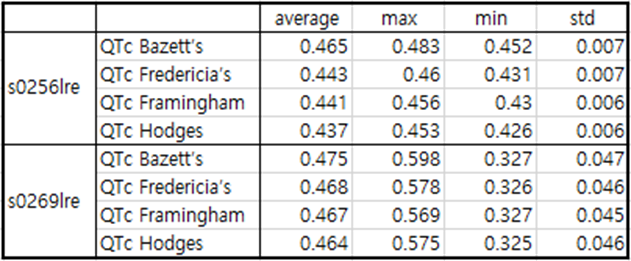
Table8 patient079
patient079 is a case of postero-lateral MI.
Immediately after MI occurs, the ECG is reversed to the extent that the T wave reaches -0.8.
The electrocardiogram taken about a month after the MI showed a flat T wave and QTc was significantly prolonged.
4. infero-postero-lateral
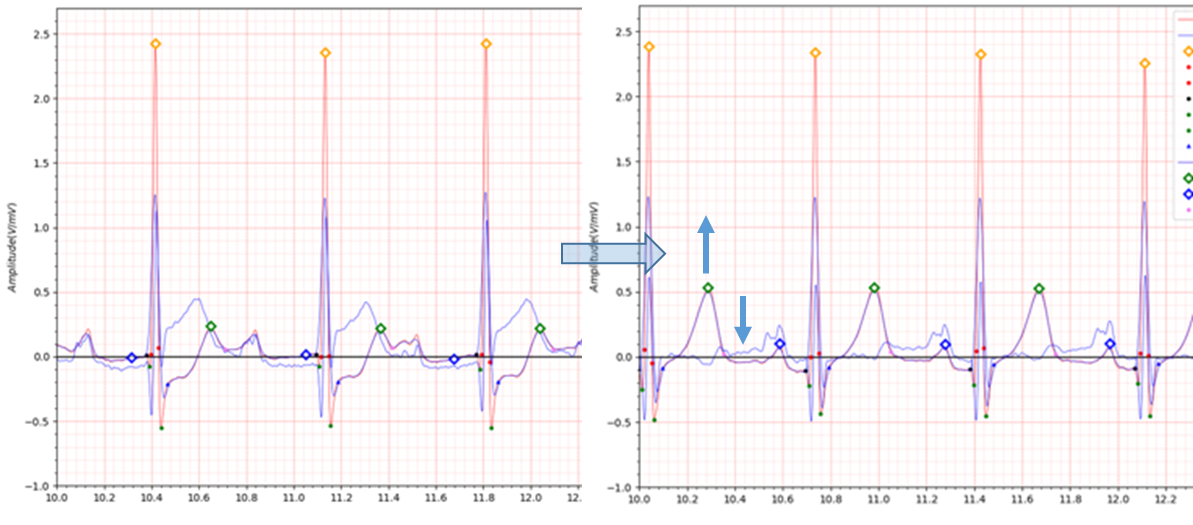
Fig.9 patient080 s0260lre: 25/02/1992 -> s0315lre: 31/07/1992
- age: 48
- sex: male
- ECG date: 25/02/1992, Infarction date (acute): 24-Feb-92
- Reason for admission: Myocardial infarction
- Acute infarction (localization): infero-postero-lateral
- Former infarction (localization): no
- Additional diagnoses: Hyperlipoproteinemia Type Iib Ventricular fibrillation
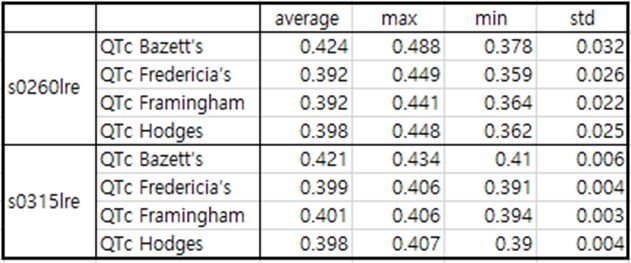
Table9 patient080
patient080 is a case of infero-postero-lateral MI.
Immediately after MI occurred, the ECG showed a depression of -0.2 at the J point.
In the electrocardiogram taken about 5 months after MI, the T wave is elevated, the Q wave has a depth of about -0.2,
and the J point has a depression of about -0.1. There is no particular abnormality in QTc.